Exploring Cutting-Edge Foam Control Technologies for Lasting Practices
Wiki Article
Effective Methods for Attaining Optimal Foam Control in Chemical Manufacturing
Efficient foam control is a vital element of chemical manufacturing that can significantly impact manufacturing performance and item high quality. By understanding the mechanisms of foam development and picking proper anti-foaming agents, manufacturers can take aggressive actions to alleviate extreme foam.Understanding Foam Formation

Surfactants, or surface-active agents, decrease the surface tension of the liquid, facilitating bubble security and advertising foam generation. In addition, agitation or blending procedures can improve bubble formation, frequently exacerbating foam concerns. The attributes of the liquid tool, including thickness and thickness, further impact foam habits; for example, even more viscous liquids have a tendency to catch air better, bring about boosted foam stability.
Comprehending these basic aspects of foam development is vital for efficient foam control in chemical production. By acknowledging the problems that advertise foam advancement, suppliers can implement targeted methods to mitigate its unfavorable results, thereby enhancing manufacturing procedures and guaranteeing constant item quality. This foundational understanding is crucial before checking out certain approaches for controlling foam in industrial setups.
Option of Anti-Foaming Representatives
When choosing anti-foaming agents, it is necessary to take into consideration the specific qualities of the chemical process and the sort of foam being produced (Foam Control). Numerous variables affect the effectiveness of an anti-foaming agent, including its chemical composition, temperature stability, and compatibility with other process materialsSilicone-based anti-foams are commonly utilized because of their high effectiveness and wide temperature variety. They work by minimizing surface tension, enabling the foam bubbles to coalesce and break more easily. However, they may not appropriate for all applications, particularly those entailing delicate solutions where silicone contamination is a problem.
On the other hand, non-silicone representatives, such as mineral oils or natural compounds, can be advantageous in certain scenarios, specifically when silicone deposits are unfavorable. These representatives have a tendency to be much less efficient at greater temperatures but can provide reliable foam control in various other problems.
Furthermore, understanding the foam's origin-- whether it emerges from aeration, agitation, or chain reactions-- overviews the choice process. Examining under actual operating conditions is critical to make certain that the selected anti-foaming representative satisfies the distinct needs of the chemical production process properly.
Process Optimization Strategies
Efficient foam control is a vital facet of enhancing chemical production processes. To boost effectiveness and minimize production prices, makers must carry out targeted process optimization methods. One essential strategy involves changing mixing speeds and arrangements. By fine-tuning these parameters, drivers can lower turbulence, therefore reducing foam development throughout mixing.Furthermore, regulating temperature level and pressure within the system can substantially influence foam generation. Lowering the temperature may minimize the volatility of particular components, resulting in reduced foam. Furthermore, maintaining optimal pressure levels assists in alleviating too much gas launch, which adds to foam stability (Foam Control).
An additional reliable strategy is the strategic addition of anti-foaming agents at crucial stages of the process. Careful timing and dosage can guarantee that these agents efficiently suppress foam without disrupting other procedure criteria.
In addition, including an organized analysis of resources residential or commercial properties can help identify naturally frothing materials, enabling for preemptive actions. Performing routine audits and procedure testimonials can reveal ineffectiveness and areas for improvement, allowing constant optimization of foam control techniques.
Monitoring and Control Equipment
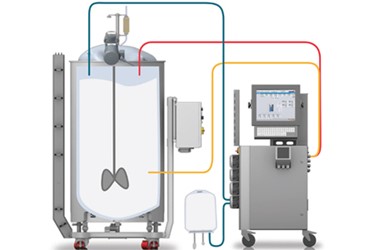
Tracking and control systems play an important role in keeping ideal foam administration throughout the chemical production procedure. These systems are important for real-time monitoring and modification of foam levels, making certain that manufacturing effectiveness is taken full advantage of while minimizing interruptions brought on by too much foam formation.Advanced sensing units and instrumentation are employed to identify foam density and elevation, offering essential data that educates control algorithms. This data-driven strategy permits the prompt application of antifoaming agents, making sure that foam degrees stay within appropriate limits. By incorporating surveillance systems with process control software program, manufacturers can carry out Look At This computerized reactions to foam variations, reducing the requirement for hand-operated intervention and improving functional uniformity.
Moreover, the combination of artificial intelligence and predictive analytics right into monitoring systems can help with positive foam monitoring. By analyzing historical foam data and functional criteria, these systems can anticipate foam generation patterns and recommend preemptive steps. Routine calibration and upkeep of surveillance tools are important to guarantee precision and integrity in foam discovery.
Inevitably, reliable monitoring and control systems are vital for optimizing foam control, promoting security, and enhancing general efficiency in chemical production atmospheres.

Case Research Studies and Ideal Practices
Real-world applications of monitoring and control systems highlight the significance of foam administration in chemical manufacturing. A notable case study involves a large-scale pharmaceutical producer that implemented an automated foam detection system.Another excellent instance originates from a petrochemical business that embraced a combination of antifoam agents and procedure optimization techniques. By evaluating foam generation patterns, the organization tailored its antifoam dose, leading to a 25% reduction in chemical usage and substantial price financial savings. This targeted approach not only lessened foam disturbance but likewise improved the overall stability of the manufacturing process.
Verdict
To conclude, accomplishing optimal foam control in chemical production requires an extensive approach incorporating the choice of suitable anti-foaming representatives, implementation of procedure optimization methods, and the integration of innovative tracking systems. Regular audits and training additionally enhance the performance of these methods, fostering a society of continuous renovation. By dealing with foam development proactively, producers can significantly improve production effectiveness and product high quality, inevitably adding to even more economical and sustainable procedures.By understanding the systems of foam development and selecting proper anti-foaming agents, producers can take aggressive steps to alleviate excessive foam. The attributes of the fluid medium, including thickness and thickness, further influence foam actions; for example, more viscous liquids often tend to trap air a lot more properly, leading to enhanced foam stability.
Recognizing these basic aspects of foam formation is crucial for reliable foam control in chemical manufacturing. By evaluating historical foam information and functional criteria, these systems can forecast foam generation patterns and recommend preemptive actions. Foam Control. Regular audits of foam control determines make sure that procedures continue to be maximized, while fostering a culture of proactive foam administration can lead to sustainable enhancements throughout the production range
Report this wiki page